
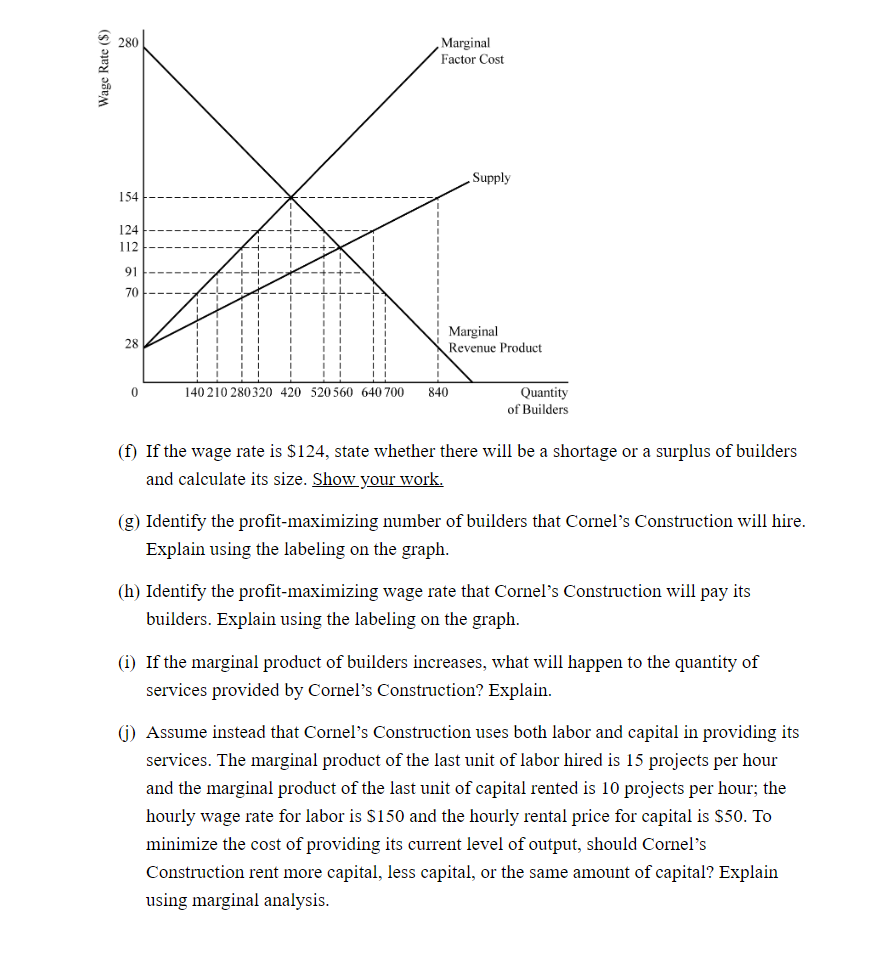
The interactive graph below allows you to shift the market demand and supply curves and see how that affects individual firms. That will increase the supply and push the price down until all firms earn zero economic profits. In the long-run, potential entrants would see the profits being earned by firms and would enter the market (since there are no barriers to entry).

P>MC, they could earn additional profits by producing more. If firms produced more than that, they would be taking a loss on the extra production. Illustrated as the green rectangle in the graph. Firms are maximizing profits when they produce up until P=MC.For market supply, we have to multiply that quantity by the number of firms in the market. Elasticity of demand at point R on the average revenue curve RT/RS. In figure 6, AR and MR are the average revenue and the marginal revenue curves. AR MR or MR AR (e/ (e-1)) where, AR Average Revenue, MR Marginal Revenue and ‘e’ price elasticity of demand. That intersection point gives how much an individual firm produces. The relationship is expressed in the formula. (Recall, for a price-taking firm marginal revenue is equal to the price.) This is illustrated in the above graph where MC (blue line) intersects the Market Price (red dashed-line). As price-takers, firms will produce where the Market Price=Marginal Cost. We can calculate Marginal Revenue by using the below formula Marginal Revenue (MR) Change in Revenue / Change in Quantity Marginal Revenue (1,95,000 1,00,000) / (3000 2000) Marginal Revenue 95,000 / 1000 Marginal Revenue 95 Marginal Revenue for Anand & Son’s Shops is 95.As the price of a good is often tied to market. The graph above illustrates the important points about a firm's profit-maximizing decision in a perfectly competitive market. Marginal revenue is a financial and economic calculation that determines how much revenue a company earns in revenue for each additional unit sold. (Intuition: imagine your grade in Econ 20A as the marginal grade, when you get an A what does it does to your grade point average?) With the production and sale of each subsequent unit of production, the company begins to make a marginal profit: The break-even formula in Excel 2016. The MC curve intersects the ATC at the minimum of ATC.But, as production increases so does average total costs as variable costs become more important. Average total costs (ATC) are decreasing in production, at first, as fixed costs are the predominant cost at low quantities.Step 2: Calculate the change in quantity. Marginal costs (MC) are increasing over the range of production relevant to firms' decision-making. It currently costs your company 100 to produce 10 hats and we want to see what the marginal cost will be to produce an additional 10 hats at 150.Recall, from the discussion of firms' cost curves:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
